Overflow
When the element content is bigger than the element boundary, overflow defines the visible behaviour on the screen.
Overflow behaviours
There are five kinds of overflow behaviours are supported:
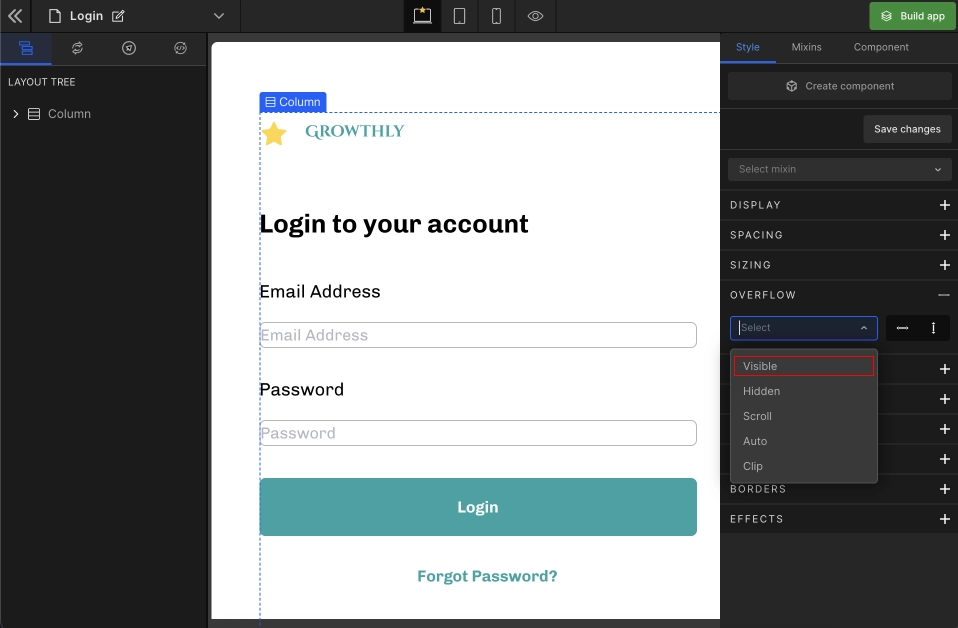
1. Visible
Displays the entire content without applying any change.
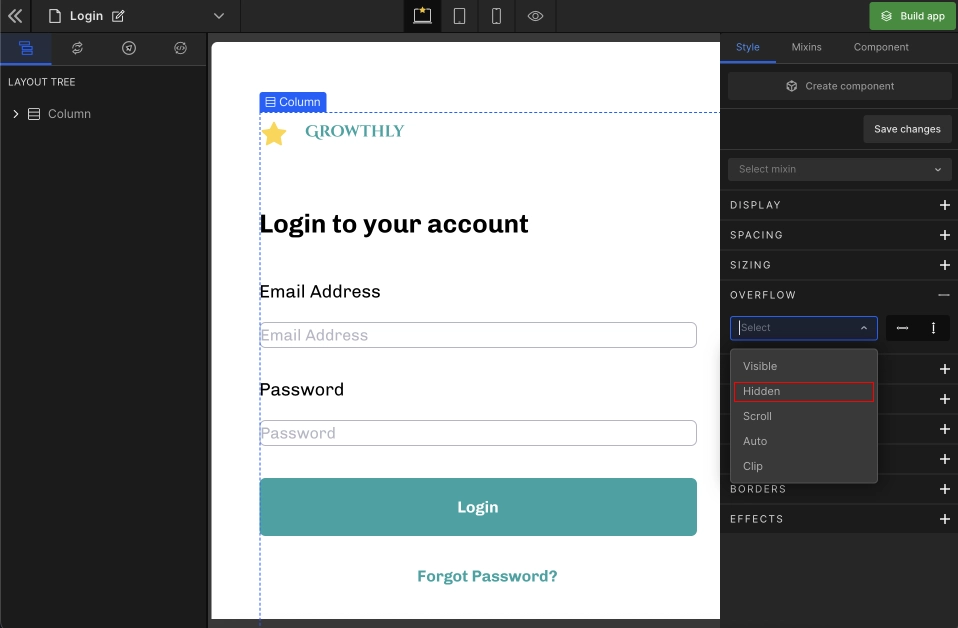
2. Hidden
Hides the content overflowing outside of the element's boundary.
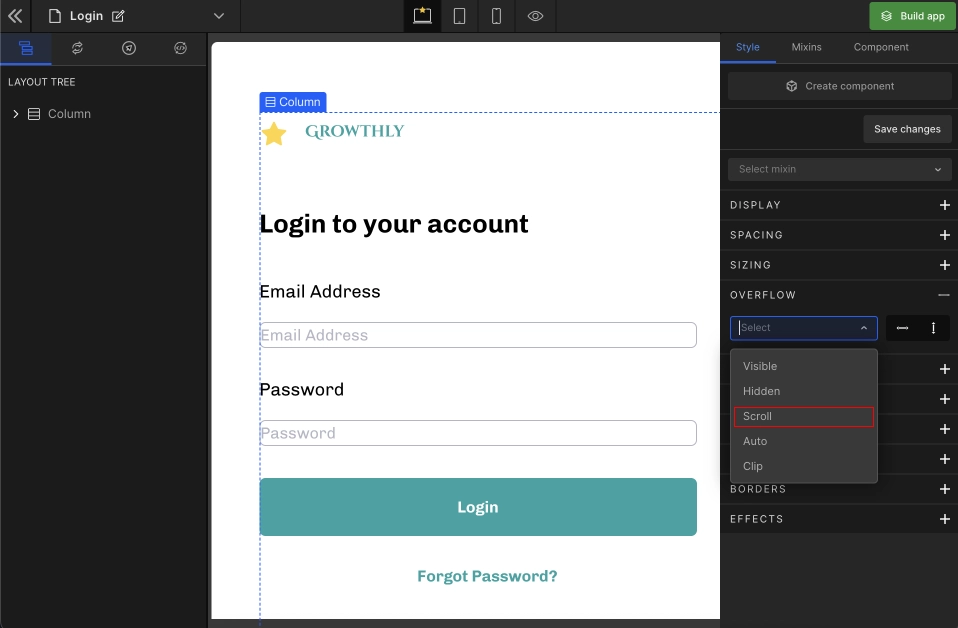
3. Scroll
When the element's content is more extensive and overflows, there will be a scrollbar to read the content.
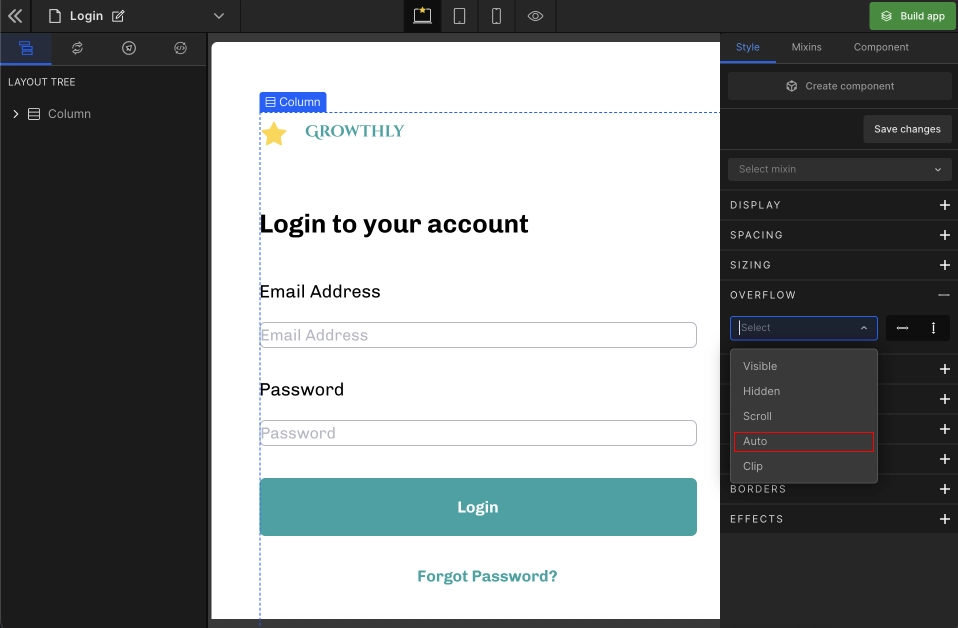
4. Auto
If the element's content fits inside its boundary, it looks the same as visible but establishes a new block formatting context.
5. Clip
Just as hidden, it clips the element's content to its boundary. The difference is that the clip forbids all scrolling and programmatic scrolling. The element is not a scroll container. Also, it does not start a new formatting context.
Overflow Direction
There are two types of overflow directions supported:
1. Overflow-X
It sets the overflow direction to horizontal.
2. Overflow-Y
It sets the overflow direction to vertical.
Got a question? Ask here.